Advances in MASLD and MASH
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is a condition where excessive fat accumulates in liver cells. It has been observed that approximately 30% of MASLD patients develop metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH). The development of the disease may lead to liver cirrhosis and possible development of hepatocellular carcinoma. This highlights MASLD as the leading cause of liver disease worldwide and its prevalence is predicted to increase by 2030 if current trends remain as today.
Recent progress in liver disease research has brought about significant progress in understanding and addressing MASLD, previously known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Collaborative efforts among leading liver disease societies have resulted in updated nomenclature and diagnostic criteria for MASLD, aiming to provide clarity and improve patient identification without stigmatization.
MASLD affects over a quarter of the global population and presents various risk factors, including obesity, impaired glucose metabolism, and high blood pressure.
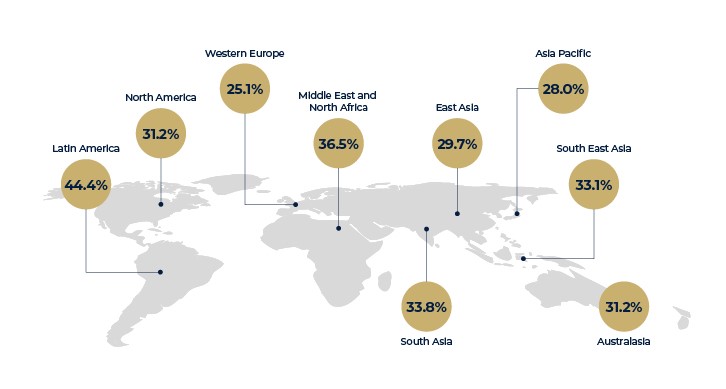
Understanding the risk factors is crucial for preventing disease progression to MASH and associated complications like liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
read more and Download white paper
As the prevalence of MASLD continues to rise globally, staying informed about the latest research and breakthroughs is essential. Download our comprehensive white paper about MASLD and MASH and discover how advancements in biomarker research are shaping the future of liver disease management.
Advances in MASLD and MASH: nomenclature, characteristics, and biomarkers – white paper

Mercodia assays for MASLD and MASH
At Mercodia, we are dedicated to supporting liver disease research with our range of assays for studying MASLD and MASH biomarkers. Our assays offer high accuracy and consistency, providing researchers with valuable tools for advancing our understanding of liver disease.